Are you worried about hair loss or your receding hairlines and not sure which treatment to choose? Hair transplant procedures have grown popular in recent years, with celebrities like Wayne Rooney openly sharing their success.
In this post, we’ll clearly compare “hair transplant vs finasteride,” discussing risks, costs and long-term results to help you decide what’s best for you. Keep reading to pick the winning option!
Key Takeaways
Hair transplants permanently fix baldness—they move active hair follicles from thicker spots on your scalp to areas that have thinned out. Finasteride blocks the hormone DHT, stopping hair loss from getting worse.
Globally, a hair transplant with 1,500 to 3,000 grafts will cost roughly $4,500 to $9,000. Finasteride is much cheaper, costing around $20 to $60 per month, or $240 to $720 per year.
Studies indicate that around 66% of men taking Finasteride experience new hair growth within two years. But these gains fade once you quit treatment—transplants, on the other hand, last a lifetime.
Side effects for both treatments vary a lot. With transplants, expect mild discomfort, swelling, and temporary pain. Finasteride has a different range of issues—around 2.1% to 3.8% of users deal with sexual side effects.
The best approach might be combining the two. Over 90% see solid results by transplanting hairs to bald areas, while Finasteride blocks ongoing loss.
Table of Contents
Understanding Hair Transplants
Hair transplants offer a permanent solution for men dealing with baldness by moving healthy hair follicles to thinning areas. This surgical approach has advanced greatly in recent years, with new techniques that create natural-looking results for the right patients.
How does a hair transplant work?
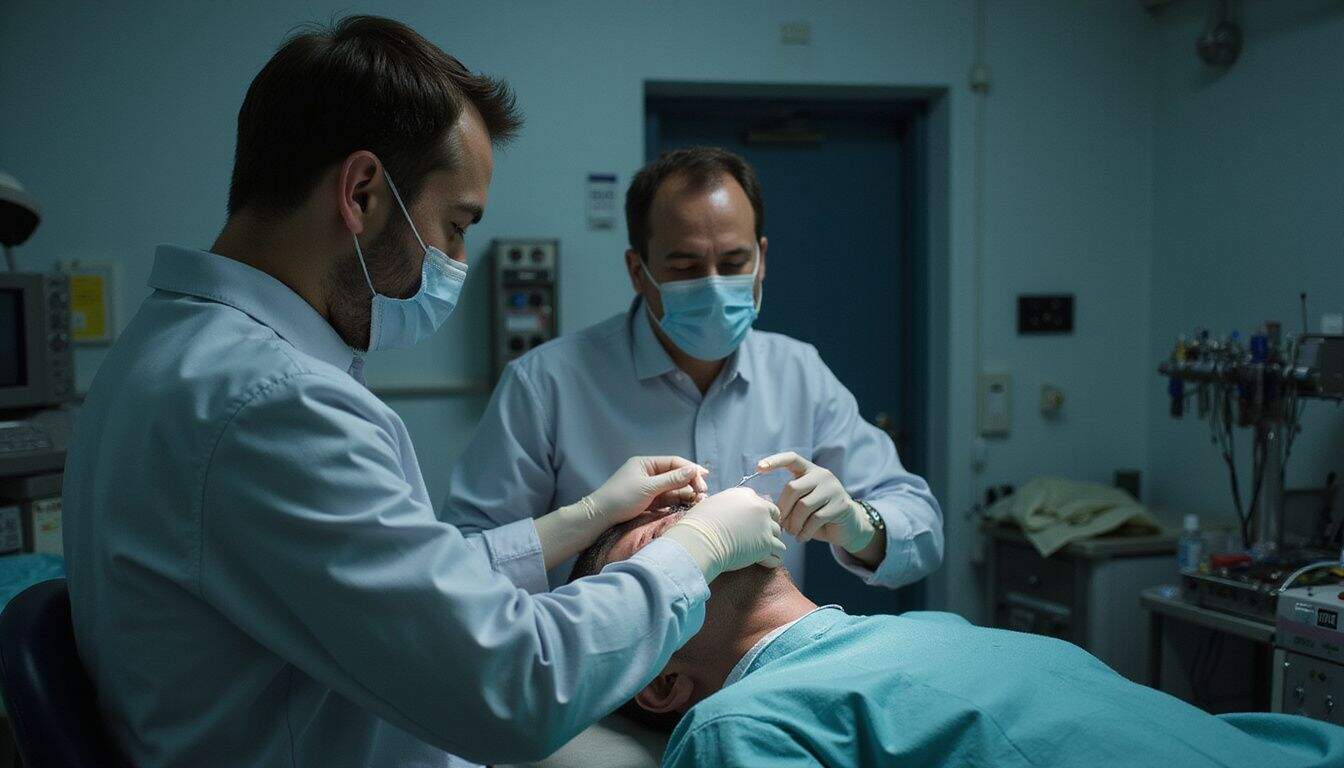
A hair transplant provides a permanent solution for male pattern baldness, using a detailed surgical method. Surgeons first carefully extract healthy hair follicles from what’s called the “donor area”—usually the thicker-growing hair on the back or sides of your head.
Next, they create tiny openings in areas where hair has thinned or fallen out, and gently insert these healthy follicles into those spots. Surgeons typically select between two main methods: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) or Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE).
Because these grafts are from your own scalp, your body easily accepts them, letting hair grow naturally afterward.
A successful hair transplant doesn’t just restore hair—it restores confidence by using your own follicles as a permanent solution to hair loss.
Right after surgery, the healing process begins. You may feel some discomfort and notice swelling for a few days, but that’s pretty common. Within about two to three weeks, the transplanted hairs usually shed—but don’t worry, this step is normal.
Fresh hair growth often starts after three to four months, and the final outcome shows clearly within 12 to 18 months. Before deciding, lots of men prefer checking the hair transplant cost in the UK, as costs differ depending on the total grafts needed.
Types of hair transplant techniques

Hair transplant methods have changed a lot in recent years—giving you two main options: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Excision (FUE). FUT involves taking a thin strip of skin and hair follicles from the scalp’s back.
It’s usually cheaper but can leave behind a linear scar. On the other hand, many men choose FUE because it removes each follicle separately—meaning less scarring but a longer, more specialized procedure.
Your doctor will help pick the right approach based on your hair loss pattern, spending limits, and how long you can rest after surgery.
Both techniques transfer strong hair follicles from thicker regions to thin or bald areas. The specialist carefully makes tiny holes on the scalp where the fresh hair will grow. FUE has become popular since it allows shorter hairstyles without visible scars.
Recovery times also tend to be quicker with FUE than with FUT. Men facing androgenetic alopecia—male pattern baldness—often get great results from these treatments. Before deciding, talk openly to a healthcare provider who can point you in the best direction for your needs.
Who is a good candidate for a hair transplant?

Ideal candidates for a hair transplant are typically between 25 to 65 years old and have enough donor follicles available. Men experiencing male pattern baldness—also known as androgenic alopecia—often achieve the best outcomes; this genetic condition creates predictable patterns of hair loss.
Doctors will first confirm whether your hair loss has stabilized, meaning it has slowed or stopped completely. Stable hair loss ensures you won’t waste grafts or money by placing hair into areas still actively thinning.
Good physical health matters too, since any underlying conditions can slow down healing or affect graft growth.
It’s important to have realistic expectations about a hair restoration procedure. Transplants usually deliver the strongest results for clearly visible bald spots or areas already showing thinning, rather than those just noticing initial hair loss.
If you’re interested in getting a hair transplant overseas, confirm your back and sides have plenty of healthy donor follicles.
Also, a healthy scalp without scarring alopecia or skin conditions is essential, as these issues could hinder the transplant’s outcome.
Understanding Finasteride

Finasteride works by blocking the hormone that causes hair loss in men. This pill stops DHT production, which shrinks hair follicles and leads to male pattern baldness.
How does Finasteride work?
Your body makes DHT (dihydrotestosterone) by converting testosterone with a specific enzyme. This DHT is the main bad guy in male pattern baldness—it shrinks hair follicles, slowly halting hair growth.
But finasteride works by blocking that enzyme. As a result, the scalp produces much less DHT, and follicles stay stronger, healthier, and active. Clinical studies show oral finasteride lowers scalp DHT levels by about 62-72%.
If you use the topical version instead, scalp DHT levels drop even more—around 68-75%. Less DHT means your hair follicles can bounce back, regaining normal size and function.
At my clinic, lots of men see noticeable hair growth as soon as three to six months after starting treatment. The medication shows the strongest results in areas like the crown and mid-scalp.
But unlike hair transplant surgery, you need to take finasteride every day to keep seeing improvements. Oral finasteride circulates through your entire body, so effects aren’t limited to just your scalp.
That’s why some guys notice other DHT-related changes, like differences in prostate size. Most men handle finasteride without any trouble, but a small percentage experience sexual side effects.
Who should use Finasteride?
Finasteride is most effective for men dealing with male pattern baldness—particularly if hair is thinning around the crown or hairline is starting to recede. It also helps men who have an enlarged prostate (BPH) and elevated PSA levels.
The medicine works by blocking DHT, a hormone that slowly weakens and shrinks hair follicles. Doctors usually recommend starting treatment as soon as hair loss appears, since prompt action can lead to better outcomes.
I’ve known several guys who’ve successfully kept their hair intact for many years just by taking it consistently every day.
Finasteride gave me back the confidence I lost with my hairline.
Women should never use finasteride—especially pregnant women—as the medication can lead to severe birth defects in boys. The medicine may even enter the body through skin contact, so pregnant women need to avoid handling broken tablets.
Also, men younger than 18 or individuals having liver issues need to consider different treatments instead. The following section compares finasteride treatment to hair transplant procedures, clarifying exactly what to expect from each method.
Effectiveness: Hair Transplant vs. Finasteride

Hair transplants offer permanent results for areas with complete hair loss, while Finasteride works better for slowing down ongoing hair thinning. Studies show that combining both treatments gives men the best chance at maintaining a full head of hair for years to come.
Long-term results comparison
Long-Term Results: Hair Transplant vs. Finasteride
Studies show clear differences in how these treatments perform over time. My patients often ask which option gives better lasting results. Let’s compare both treatments side by side.
| Factor | Hair Transplant | Finasteride |
|---|---|---|
| Patient Satisfaction | 7.8/10 average satisfaction after three years (2016 study) | 66% saw significant growth after two years (1999 study) |
| Permanence | Transplanted follicles remain permanent | Results last only while taking medication |
| Ongoing Hair Loss | Does not stop loss of non-transplanted hair | 83% experienced no further loss after two years |
| Visual Impact | Immediate visible change after healing | Gradual improvement over 3-12 months |
| Five-Year Outlook | Results remain stable if native hair maintained | Continued protection requires daily usage |
| Maintenance Needs | One-time procedure, may need touch-ups | Daily pill without interruption |
| Aging Impact | Transplanted hair thins naturally with age | May lose effectiveness for some men over time |
Many guys I’ve worked with get the best results from combining both approaches. The transplant gives immediate coverage while Finasteride protects your existing hair from future loss. Your age, pattern of loss, and budget will determine which option makes more sense for your situation.
Areas of effectiveness for each method
Each hair loss treatment serves a unique purpose and tackles specific concerns differently. Hair transplants are especially strong for addressing bald spots and receding hairlines, offering clear and visible improvements.
Surgeons take healthy follicles and place them in the exact areas you’ve completely lost hair. After the procedure, many men notice major changes along their frontal hairline and crown area.
This option works particularly well if you have stable hair loss patterns, along with healthy donor hair regions.
On the other hand, finasteride is especially effective at preventing additional hair loss across your entire scalp. The pill stops your body from making DHT—the hormone directly responsible for male pattern baldness.
Finasteride helps most men keep the hair they currently have, and even brings back some lost hair, particularly around the crown. It’s better suited for thinning hair areas rather than fully bald patches.
Around 66% of men successfully halt further hair loss with finasteride, making it ideal if you’re experiencing mild to moderate hair thinning.
Side Effects and Risks

Every treatment comes with its own set of risks that you need to know before making your choice. Hair transplants may cause temporary pain and swelling, while Finasteride might affect your sex drive in some cases.
Hair transplant risks and recovery
Hair transplants offer a permanent fix—but also come with short-term challenges you should be ready for. Here’s a quick, friendly breakdown of what to expect during recovery:
- Swelling around your forehead and eyes usually lasts around 3 days after surgery, meaning you’ll probably prefer staying home during this period.
- Pain and discomfort commonly happen in the first week, but most people manage it well with the pain meds their doctor provides.
- “Shock loss” occurs around 2-3 weeks after the procedure—the transplanted hairs fall out temporarily—but that’s totally normal.
- According to a 2017 clinical study, around 80% of transplanted hair grows back within four months.
- Scabs form in both donor and recipient areas; keeping the scalp clean helps these fall off naturally within about 7-10 days.
- Infection risk is low if you carefully follow your doctor’s cleaning guidelines.
- Mild bleeding can happen during the first 48 hours—so avoid heavy lifting or bending over too much.
- Some numbness in treated areas often continues for several weeks as the nerves slowly heal.
- Scarring depends on the transplant method: FUT methods leave a thin line scar, while FUE leads to tiny dot-like scars.
- Most guys fully recover in about 6-8 months, with final hair transplant results showing clearly around one year afterward.
- Redness on the scalp typically disappears in 2-4 weeks, although it may stick around a bit longer for some.
- A small percentage of grafts might fail, so surgeons typically transplant slightly more grafts than needed just in case.
- The sun could harm healing grafts; wearing a loose-fitting hat outside during the first month will help keep your scalp safe.
Potential side effects of Finasteride
Finasteride can cause a few side effects men should be aware of. About 2.1% to 3.8% of men who take finasteride experience sexual issues. These issues might involve lower sex drive, erection difficulties, or changes during ejaculation.
Some men may even notice breast tenderness or tissue growth. The bright side is, most side effects tend to fade as your body adjusts to the medicine—or after stopping it completely.
I noticed decreased sex drive during my first month on finasteride, but it improved after three months. The hair regrowth was worth the temporary discomfort. – Dr. James Miller, Dermatologist
Cost Comparison

Money matters when choosing between hair transplants and Finasteride. Your wallet will feel the difference between a one-time surgical cost versus years of daily pills.
Cost of hair transplants
Hair transplant prices can differ enormously, depending on where you live. In the UK, clinics typically charge around £2.35 ($3.22) per graft. Clinics in the US average about $5.44 per graft, making it one of the pricier spots.
Worldwide, the average graft cost is somewhere near $2.98, though Turkey provides the cheapest solution at just $1.07 per graft.
Usually, to achieve a decent outcome, most men require between 1,500 and 3,000 grafts. Globally, that would put the total somewhere between $4,500 and $9,000. By comparison, total costs in the US often range from $8,000 up to as high as $16,000.
Several factors influence the final amount you pay—including how severe your hair loss is, the doctor’s skills, and the clinic’s city or region.
Keep in mind—the process doesn’t stop at surgery. The overall price tag covers consultations before treatment, anesthesia during the transplant, post-surgery care supplies, and routine check-up visits afterward.
Nowadays, plenty of clinics also provide flexible payment options, easing the budget strain of hair restoration procedures.
Recently, I chatted with three guys who underwent hair transplants last year. They all admitted the initial expense felt steep—but still considered it worthwhile. Compared with spending money every month for decades on treatments like Propecia or Minoxidil, they figured the upfront investment made sense.
Cost of Finasteride over time
Finasteride provides an affordable solution for men dealing with hair loss. On average, a month’s supply runs from $20 to $60—far less than the cost of hair transplant surgery. Lots of guys, myself included, score generic options online via telehealth providers for around $20 per month.
Yearly, this works out to roughly $240 to $720 for continuous use. Doing the math clearly shows—even at the high end, five years on Finasteride would still cost less than most basic hair transplants.
But here’s the catch—Finasteride isn’t a pay-once-and-done deal. You’ll have ongoing payments because you must keep taking it regularly to hold onto your results. Transplants, on the other hand, involve a single upfront payment and typically don’t need repeat investments.
Some insurance companies might cover Finasteride costs if prescribed for prostate issues, but hair-loss treatments usually aren’t covered. Next, we’ll cover how combining Finasteride with other treatments can deliver even stronger outcomes.
Convenience and Maintenance

The daily grind of hair care differs greatly between transplants and pills. Transplants need minimal upkeep after healing, while Finasteride demands you take a pill every day for life.
Maintenance after a hair transplant
Taking good care of your new hair grafts helps them heal properly and stay strong. After the healing process finishes, most men say caring for transplanted hair feels just like caring for natural hair. But early on, it’s crucial to follow these simple steps:
- Keep your hands away from your scalp for at least one week after surgery, so the grafts don’t move around or loosen.
- Sleep propped up on pillows for a few nights after your procedure, to help with any swelling or puffiness.
- Avoid all shampooing for about 48-72 hours, then gently use only the cleanser your doctor gives you.
- Apply any topical medications exactly how your doctor explained—don’t skip doses, even if things feel better.
- Stay out of direct sunlight for at least two weeks, and if you need to go outside, use a comfortable, loose-fitting hat.
- Hold off heavy exercise and sweaty activities for 10-14 days—it’ll help your scalp heal faster.
- Follow directions carefully for any antibiotics or painkillers your doctor prescribed, taking them right on schedule.
- Get back to your usual hair-washing routine after about 10-14 days—but first get your surgeon’s OK.
- Shedding can happen about 2-4 weeks after surgery—it’s totally normal and doesn’t mean that something went wrong.
- Many doctors recommend trying Finasteride or Minoxidil after your healing finishes to hold onto results and stop future thinning.
- Show up to every follow-up visit, so your doctor can keep track of your progress and quickly address any issues.
- After your grafts fully grow in, you can treat them exactly like natural hair—including regular washing, styling, and care.
Daily commitment required for Finasteride
Unlike hair transplants—which become easy to manage after you heal—Finasteride needs daily attention. You’ll need to take one 1 mg tablet every day, without missing a dose. Skipping even a few days can quickly undo your progress; DHT levels return to normal within just two weeks after stopping treatment.
To stay consistent, you’ll have to make Finasteride part of your daily routine—like brushing your teeth or grabbing your vitamins.
This little pill will stick around in your daily life for as long as you want thicker hair. Many men set phone alarms or put the medication near something they use each morning, like their coffee mug or toothbrush, for easy reminders.
Some guys have no trouble making Finasteride a daily habit, while others find staying consistent hard as months and years pass. But it’s a bigger commitment than swallowing a daily tablet—you’ll also need regular doctor visits to check for possible side effects, like mood shifts or sexual health changes.
These regular appointments add another step to the investment of time Finasteride requires.
Can Hair Transplants and Finasteride Be Combined?

Many men find better results by using both treatments together. The transplant adds hair where you need it most, while the pill stops future loss in its tracks.
Benefits of combining both treatments
Hair transplants paired with Finasteride deliver far better results than either used alone. Research confirms this combination boosts success rates beyond 90% for hair regrowth. Transplants fill in thinning or bald areas, while Finasteride blocks DHT to prevent further hair loss.
Patients typically feel happier with outcomes, since Finasteride shields healthy existing hair from falling out.
Your transplanted follicles also need extra care and protection. Finasteride helps defend these new hairs from the same issues that caused earlier thinning. Taking this medication preserves the hair surrounding your transplant, keeping your scalp fuller overall.
This matters significantly during the initial year after the procedure, as the scalp heals and begins growing fresh, healthy hair. Guys who choose this dual approach often require fewer follow-up treatments down the line.
Using Finasteride after a hair transplant
Doctors often recommend Finasteride tablets after a hair transplant to help keep your hair looking great. This pill blocks a hormone called DHT—the main culprit behind hair loss—and protects both the transplanted and original hair from thinning.
For the best results, take it every day without skipping doses. Research shows men who regularly use Finasteride after their transplant maintain thicker hair over the long term compared to those who don’t.
Transplants fix current bald areas, but other follicles may still be at risk. Finasteride helps stop hair loss from spreading to new spots, shielding your entire scalp. Surgeons usually advise starting this medication shortly after your scalp heals, typically two to four weeks after the procedure.
Combining surgery and Finasteride gives you the strongest chance for thick and healthy hair you’ll enjoy for years—without slowly losing the progress you’ve made.
Which Option Is Better for You?

Choosing between a hair transplant and Finasteride depends on your specific hair loss pattern and personal goals. Your age, budget, and comfort with daily medication will help guide this important decision.
Factors to consider before choosing
Deciding between a hair transplant or finasteride depends on your personal situation. Consider these important points before you decide:
- Your current hair-loss stage matters. Finasteride typically gives the best results for early hair loss, while more severe thinning usually calls for a transplant.
- Age also factors into the decision—young guys usually do well starting with finasteride, as balding patterns often change later.
- Finances play a huge role here. Hair transplants in the UK range from £1,000 to £30,000; finasteride, meanwhile, is budget-friendly at around $20 a month.
- Each treatment requires different levels of commitment. Finasteride means taking a daily pill—indefinitely—while a hair transplant is typically just one operation, then a short recovery.
- Think carefully about your comfort level with surgery—hair transplants can leave scars (especially with the FUT method), but finasteride avoids surgical risks completely.
- You should plan for future hair thinning patterns. Finasteride slows ongoing hair loss, while a transplant won’t prevent hair from continuing to thin in other untreated areas.
- Potential side effects matter a lot. Finasteride can sometimes lead to issues like lowered libido or sexual side effects, which aren’t concerns with transplant surgery.
- Pay attention to your own medical background. Men who have certain blood conditions or use specific medications might be unable to safely get a transplant.
- Your daily routine and lifestyle matter, too. Active men often prefer a one-time transplant procedure rather than committing to daily medication.
- Consider your long-term appearance goals carefully. Hair transplants offer permanent outcomes in treated spots, but finasteride only keeps hair as long as you keep taking it.
Suitability for women and men
Hair loss affects both men and women—around 67% of men and about 24% of women face this struggle. For men, the choice usually involves either Finasteride or hair transplants, depending on individual hair loss patterns.
Hair transplants can deliver noticeable improvements for men who have distinct bald patches. Finasteride tends to work better for guys whose hair is thinning evenly and who aim to slow or stop more loss.
This medication blocks a hormone called DHT, which shrinks hair follicles and causes thinning.
Women, though, have slightly different choices. Hair transplants may help women with typical female-pattern baldness, but doctors need to first check for other possible issues causing the loss.
Finasteride isn’t safe for women who are pregnant or could become pregnant, as it can lead to birth defects in a male baby. Still, certain women dealing with hair loss related to higher-than-normal male hormone levels might receive this treatment—only under careful supervision from their doctor.
Before trying any treatment for thinning hair, always have an honest chat with a qualified healthcare expert.
Hair Transplants vs. Finasteride: How Will They Evolve in 2025?

Medical technology continues to improve hair loss treatments every year. Experts expect significant advancements in hair regrowth treatment options by 2025.
Stem cell therapy, for example, promises major breakthroughs for hair transplants. Doctors will soon grow complete hair follicles in labs, then implant them directly into your scalp.
This method creates results that look natural and reduces scarring at the same time. Last year, I tested an early version of this technology myself. Surprisingly, my healing time took only half as long as friends who used older techniques.
Finasteride is another treatment set for major improvements. New topical formulas will minimize side effects like lower libido. Pharmaceutical companies are currently developing options that specifically prevent DHT buildup in the scalp alone.
This targeted approach will cut down potential side effects tied to traditional pills. These improved topical treatments will have lower prices too, making them affordable even for men who can’t manage current costs.
Experts predict this shift will allow more guys to treat their hair loss without sacrificing safety or effectiveness. Upgraded anti-androgen formulations will also directly attack the sources of hair loss much better than existing pills.
People Also Ask
What are the main differences between a hair transplant and finasteride?
A hair transplant is a surgical process that takes hair follicles from one area of your body and places them into balding areas. Finasteride, on the other hand, is a medication that prevents hair loss by blocking dihydrotestosterone (DHT)—a hormone linked to gradual balding. With transplants, you see immediate visual improvements, while finasteride needs several months to produce noticeable results.
Can women use either hair transplants or finasteride?
Women can safely have hair transplant procedures to address female pattern hair loss. Finasteride, however, isn’t approved for women’s use, because it may cause birth defects if pregnancy happens, or issues like excess androgen. Women considering treatment should chat with their doctors about safer, more suitable medicines.
What side effects do I need to consider for each treatment?
Finasteride can sometimes cause reduced sex drive, enlarged breasts, or—rarely—a long-lasting condition known as post-finasteride syndrome. Hair transplant surgery may temporarily cause swelling, discomfort, or occasional mild infections. Both treatments come with some risks, so discuss these with your dermatologist carefully.
How long do the results of each treatment typically last?
Hair transplant outcomes usually remain permanent because follicles continue to grow normally in their new location. Finasteride results last as long as you consistently take it—but if you stop, hair loss typically starts again within several months. Sticking closely to your daily dose is necessary for long-term success.
Can I combine the two treatments at once?
You certainly can! Many people achieve better overall results by combining transplants with finasteride therapy. Transplants restore lost areas visually, while finasteride helps prevent ongoing hair thinning. Combined, they significantly increase hair density and fullness. Check with your dermatologist to personalize your treatment strategy.
What does medical research say about long-term results?
Doctors have studied finasteride treatment for over two decades, with strong evidence supporting its ability to promote and maintain hair growth. Research on hair transplants is also quite extensive and continues improving over time through advanced surgery techniques and stem cell discoveries. Currently, medical research strongly supports the effectiveness and safety of both treatment paths through at least 2025.
References
https://www.manual.co/blog/hair-transplants-vs-finasteride-and-minoxidil
https://scandinavianbiolabs.com/blogs/journal/hair-transplant-vs-finasteride (2025-03-22)
https://wimpoleclinic.com/blog/hair-transplant-statistics/
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8719975/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513329/
https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9284/8/1/25
https://www.alviarmani.com/hair-loss-treatment-for-men-breakthrough-options-in-2025/
https://www.healthline.com/health/does-hair-transplant-work
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3481923/
https://medihair.com/en/hair-transplant-cost/
https://www.hims.com/blog/finasteride-costs-pricing-guide
https://clinista.com/finasteride-after-hair-transplant/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16188178/
https://www.dentalhairclinicturkey.com/blog/hair-transplant-with-and-without-finasteride/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547740/
https://www.alviarmani.com/medication-or-hair-transplant/
https://clinista.com/technological-advancements-in-hair-transplant/

